Gate valves are essential components in controlling fluid flow across a wide spectrum of industrial applications. This article provides an in-depth overview of gate valve types, operational principles, and critical selection criteria. From steam systems in power plants to slurry lines in mining, discover how specialised gate valves enhance reliability and performance in complex systems.
Understanding Gate Valve Technology
Gate valves operate using a gate or wedge-shaped disc that moves perpendicular to the fluid flow. When fully open, they provide minimal resistance to flow, making them ideal for applications requiring unrestricted fluid passage. Their straightforward design ensures reliable performance across diverse operational environments, contributing to their widespread adoption in critical infrastructure systems.
Specialised Gate Valve Designs
- Knife Gate Valves
- Key Features:
- Thin, sharp-edged gate design that slices through suspended solids
- Compact face-to-face dimensions for space-constrained installations
- Self-cleaning action during closure
- Available in unidirectional and bidirectional configurations
- Ideal Applications:
- Pulp and paper manufacturing, mining, wastewater treatment, food processing, chemical slurries
- Pulp and paper manufacturing, mining, wastewater treatment, food processing, chemical slurries
- Key Features:
- Parallel Slide Gate Valves
- Key Features:
- Self-adjusting discs to handle thermal expansion
- Pressure-assisted sealing
- Reduced operational friction
- Suitable for horizontal and vertical installation
- Ideal Applications:
- Steam systems, power generation, refinery operations, district heating, industrial pipelines
- Steam systems, power generation, refinery operations, district heating, industrial pipelines
- Key Features:
- Wedge Gate Valves
- Key Features:
- Mechanical wedging action for superior sealing
- Solid, flexible, and split wedge variants
- Resilient seat materials
- Bidirectional flow capability
- Wedge Types:
- Solid Wedge: Robust and general-purpose
- Flexible Wedge: Handles thermal variation
- Split Wedge: Accommodates seat irregularities
- Ideal Applications:
- Water distribution, fire protection, oil & gas, HVAC, industrial cooling
- Water distribution, fire protection, oil & gas, HVAC, industrial cooling
- Key Features:
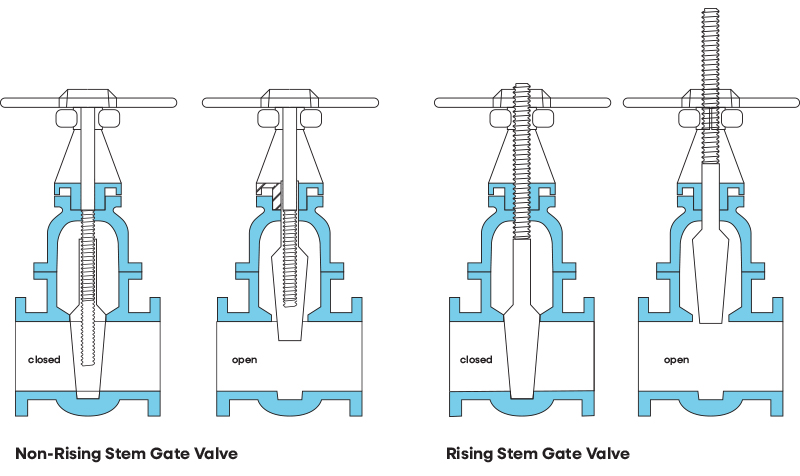
- Non-Rising Stem Gate Valves
- Key Features:
- Rotating stem with internal gate threads
- Compact vertical profile
- Stem in contact with process fluid
- Optional position indicators
- Ideal Applications:
- Underground utilities, building interiors, confined mechanical spaces, retrofit projects
- Underground utilities, building interiors, confined mechanical spaces, retrofit projects
- Key Features:
- Rising Stem Gate Valves
- Key Features:
- External stem threads with visible movement
- Stem isolated from media
- Clear operational status indication
- Enhanced control accuracy
- Ideal Applications:
- Critical process control, clean rooms, corrosive media, hazardous materials, high-cycle systems
- Key Features:
Critical Industrial Applications of Gate Valves
- Oil and Gas Industry
- Wellhead control, pipeline sectioning, tank farm management, emergency shutdowns
- API 6D/600, fire-safe design, ISO 15848 emissions control, ANSI 2500+ pressure ratings
- Water and Wastewater Treatment
- Main line isolation, treatment facility control, pump stations, filter backwash
- AWWA C500/C509/C515, NSF 61, corrosion-resistant coatings, resilient seating
- Chemical and Petrochemical
- Batch isolation, transfer lines, loading/unloading, hazardous material handling
- High alloy materials (Hastelloy, titanium), chemical-compatible seats, emissions control
- Power Generation
- Boiler isolation, steam line control, condensate return, turbine bypass
- ASME B16.34, high-temperature resistance, Stellite hard-facing, extended bonnets
- Additional Industries: Mining, pulp & paper, food & beverage, pharmaceuticals, marine, HVAC, fire protection
Choosing the Right Gate Valve: Key Considerations
- Material Selection:
- Carbon Steel: General service
- Stainless Steel: Corrosive/sanitary
- Bronze/Brass: Plumbing
- Cast Iron: Non-critical water service
- Exotic Alloys: Severe service
- Operational Parameters:
- Pressure and temperature limits
- Flow requirements and pressure drop
- Actuation method (manual, electric, pneumatic, hydraulic)
- Cycling frequency
- Installation Considerations:
- Space and clearance
- Pipeline configuration
- Connection types
- Accessibility
- Structural support
Gate Valve Seating Options
Gate valves employ different seating configurations based on service conditions and media characteristics:
- Resilient Seated Gate Valves:
- Flexible elastomeric seat materials (e.g., EPDM, NBR)
- Provide bubble-tight shutoff
- Excellent corrosion resistance and sealing
- Ideal for potable water and wastewater applications
- Metal Seated Gate Valves:
- Machined metal-to-metal contact between gate and seats
- High temperature and pressure capability
- Suitable for abrasive, corrosive, or high-pressure media
- Often hard-faced with materials like Stellite for durability
- Combination (Elastomer-Metal) Seated:
- Hybrid designs that combine metal backing with a resilient seal
- Improved sealing performance under variable conditions
- Common in utilities requiring both durability and leak-tightness
- Specialised Seats:
- Cryogenic seats for ultra-low temperatures
- Chemical-resistant polymers (PTFE, PFA) for aggressive media
- Pressure-energised seals for high-pressure systems
Gate Valve Sizes and Pressure Ratings
Gate valves are available in a wide range of sizes and pressure classes to accommodate diverse system requirements:
- Size Ranges:
- Standard sizes range from DN15 (1/2″) to DN1800 and larger
- Large-diameter valves (>DN600) commonly used in municipal, power, and water infrastructure
- Custom sizes available for specialised applications
- Pressure Classes:
- ANSI Classes: 150, 300, 600, 900, 1500, and 2500
- PN Ratings (Europe and Australasia): PN10, PN16, PN25, PN40, and higher
- API Pressure Ratings: Used in oil and gas, compliant with API 600/6D
- Selection Considerations:
- Pressure-temperature rating must match application conditions
- Valve body and bonnet materials affect pressure capacity
- Sealing type (resilient vs. metal-to-metal) impacts max pressure rating
- Common Standards for Pressure/Size Classification:
- ASME B16.34 (USA)
- EN 1092-1 (Europe)
- AS/NZS 4087 and AS 1628 (Australia/New Zealand)


Advanced Gate Valve Technologies
Automation and Control:
- Smart actuators with position feedback
- SCADA integration for remote operation
- Partial stroke testing for ESD systems
- Predictive maintenance via sensors and AI
- Wireless control and diagnostics
- Innovative Sealing Technologies:
- Metal-to-metal seats (for >400°C)
- Resilient seats for general service
- Pressure-assisted sealing
- Hard-faced surfaces for erosion
- Cryogenic-rated seals for ultra-low temps
- Emerging Trends:
- 3D printing for rapid prototyping
- Graphene/ceramic coatings for chemical protection
- Eco-friendly lubricants and sealing materials
Maintenance and Longevity Considerations
- Common Issues:
- Leakage past gate, stem galling, seat wear, packing failure
- Preventive Practices:
- Regular lubrication and actuation
- Seat and packing inspections
- Actuator and indicator calibration
- Troubleshooting Tips:
- Verify position with indicator or actuator feedback
- Inspect for obstructions or buildup
- Replace or recondition worn components
The Strategic Importance of Gate Valves in Infrastructure
Gate valves support critical reliability, safety, and operational efficiency in complex systems:
- System Reliability: Robust shutoff capability
- Operational Efficiency: Low pressure drop
- Maintenance Flexibility: Segment isolation
- Safety Management: ESD system integration
- Environmental Protection: Emission control
Expert Valve Selection and Implementation
- Engineering Evaluation: Comprehensive review of system parameters
- Total Cost of Ownership: Long-term value, not just purchase price
- Lifecycle Planning: Durability, maintenance cycles
- Performance Testing: In-house or third-party verification
- Installation Best Practices: Proper alignment, torque settings, support structures
The Future of Gate Valve Technology
As industrial processes become more demanding and efficiency-driven, gate valve design continues to evolve. Advancements in materials science, sealing technologies, and smart automation are reshaping how these essential components are engineered and applied.
At John Valves, we combine decades of experience with cutting-edge valve solutions tailored to your specific needs. Whether upgrading legacy infrastructure or specifying valves for new developments, our expert team is ready to help you maximise performance, reliability, and longevity in every system.
Contact John Valves for expert consultation and customised gate valve solutions.

